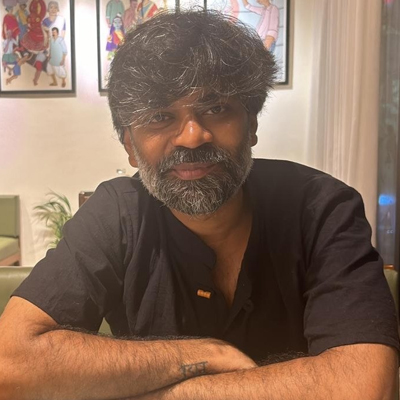
Providing training in cultivating chilli, tomato, cotton, and banana
Enhancing agricultural productivity and generating income for the farmers
Resource conservation techniques
Providing training in cultivating chilli, tomato, cotton, and banana
Within the framework of farmers’ field schools, training sessions are provided to equip farmers with the necessary skills for cultivating crops, including chilli, tomato, banana, cotton etc. Additionally, demonstration sessions are conducted to familiarize farmers with sustainable agricultural practices, such as mulching, crop rotation, and integrated pest management. For instance, innovative technologies like PB Knot are introduced, offering eco-friendly solutions for the effective management of Pink Bollworm (PBW) in cotton cultivation. These initiatives aim to enhance agricultural productivity while promoting environmental conservation and long-term sustainability.
Enhancing agricultural productivity and generating income for the farmers
Skill development initiatives have empowered farmers to adopt sustainable agriculture methods, leading to the successful cultivation of bananas and subsequent increase in income flow. This project has proven particularly beneficial for all categories of farmers, with a notable impact on small and marginalized farmers. By imparting essential skills and knowledge, farmers can effectively implement sustainable practices, resulting in improved crop yields and enhanced agricultural productivity. This approach not only strengthens farmers’ livelihoods but also contributes to the overall economic development of rural communities. Additionally, the adoption of sustainable methods fosters environmental stewardship, ensuring the long-term viability of agricultural practices for future generations.
Resource conservation techniques
Zero-energy cold storage facilities are established to extend the shelf life of vegetables, providing farmers with more flexibility in marketing and reducing forced selling, thereby enhancing economic returns. Additionally, alternative farming methods are introduced, including intensive and low-input cropping, as well as resource conservation techniques like mulching, polyhouse farming, and soilless cultivation. Through these methods, farmers acquire skills in water conservation and are equipped to address field challenges effectively.